dy/(y^2y) = dx but 1/(y^2y) = 1/(y1) 1/y, so (1/(y1) 1/y)dy = dx ln(y1) ln y = xk ln ((y1)/y) = xk (y1)/y = e^(xk) = e^k * e^x = ce^x y1 = cye^x y(1ce^x) = 1 y = 1/(1ce^x) Hmmm Wolframalpha says y = ce^x/(e^cx1) but they are the same, since u/(u1) = 1 1/(u1) so there's just a different constant c Still, better doublecheck my math Transcript Ex 96, 10 For each of the differential equation given in Exercises 1 to 12, find the general solution ( ) / =1 Step 1 Put in form / Py = Q or / P1x = Q1 (x y) / = 1 Dividing by (x y), / = 1/(( )) / = ( ) / x = / ( 1) x = Step 2 Find P1 and Q1 Comparing (1) with / P1x = Q1 P1 = 1 and Q1 = y Step 3 Find Integrating factor, IFView Ejercicios Unidad 1docx from ITI 1234 at Polytechnic University of Victoria, Ciudad Victoria EJEMPLOS METODO DE VARIABLE SEPARABLES y '=xy dy =xy dx dy =xdx y ∫ dy = xdx y ∫ ln
How To Solve X Y 1 Dy X Y 1 Dx Quora
(y ln x)^-1 dy/dx=(x/y+1)^2
(y ln x)^-1 dy/dx=(x/y+1)^2- Solve the given differential equation by separation of variablesy ln x * (dx/dy) = (y1)/x^2;Simple and best practice solution for (y (ln (x)ln (y)))dx (xln (x)xln (y)y)dy=0 equation Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework




Solved The General Or Particular Solution As Corresponds 1 Sx 4y Dx 4x 8y3 Dy 0 2 Ex Y Dx 2 X Yey Dy 0 Y 0 1 3
1 (x ylny ylnx) dx x(lny lnx) dy= 0 2 (x csc y/x y) dx xdy=0 3 (x^2 2xy 4y^2) dx ( x^2 8xy 4 y^2)=0 4 x^y ' = 4x^2 7xy 2 y^2\frac{dy}{dx}=1x^2y^2, Given Here, \frac{dy}{dx} represents the derivative of y with respect to x I will solve for x and y, treating y as a function of x (essentially y=f(x)) \int \frac{dy}{dx}dx=\int 1x^2y^2dxQuestion Solve the given differential equation by separation of variablesy ln x * (dx/dy) = (y1)/x^2 This problem has been solved!
Y = ln x then e y = x Now implicitly take the derivative of both sides with respect to x remembering to multiply by dy/dx on the left hand side since it is given in terms of y not x e y dy/dx = 1 From the inverse definition, we can substitute x in for e y to get x dy/dx = 1 Finally, divide by x to get dy/dx = 1/x We have proven theSolve the given differential equation by separation of variables y ln(x) dx dy = y 1 x 2A first order Differential Equation is Homogeneous when it can be in this form dy dx = F ( y x ) We can solve it using Separation of Variables but first we create a new variable v = y x v = y x which is also y = vx And dy dx = d (vx) dx = v dx dx x dv dx (by the Product Rule) Which can be simplified to dy dx = v x dv dx
(1 X) (1 Y2) Dx (1 Y) (1 X2) Dy = 0 CBSE CBSE (Science) Class 12 Question Papers 1851 Textbook Solutions MCQ Online Tests 31 Important Solutions 4564 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes & Videos 725 Time Tables 18 Syllabus Advertisement Remove allLearn how to solve differential equations problems step by step online Solve the differential equation dx/dy=(x^2y^2)/(1x) Group the terms of the differential equation Move the terms of the x variable to the left side, and the terms of the y variable to the right side of the equality Integrate both sides of the differential equation, the left side with respect to y, and the right side Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange




What Is The Differential Equation Of Y Ln X Dx Dy Y 1 X 2 Brainly In



Math Utoledo Edu
The solution of the differential equation `e^(x) (y1) dy (cos^(2) x sin 2x) y (dx) = 0` subjected to the condition that y = 1 when x = 0 is asked in Differential Equations by PoojaBhatt ( 994k points)First dy/dx = (y/x 1)/(y/x 1) Taking y = vx dy/dx = v xdv/dx Therefore, dx/x = (v 1)dv / (v^2 1) Integrating we get log (1/x) logc = arctan (y/x) 1/2 log How to show that \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{dy}{d(xc)}?Move the terms of the y variable to the left side, and the terms of the x variable to the right side of the equality Integrate both sides of the differential equation, the left side with respect to y, and the right side with respect to x Solve the integral \int\frac{1}{y^21}dy and replace the result in the differential equation




Solved The General Solution Of Dy Dx Xy 2 X Y Is In Chegg Com



Lcps Org
and so y = lnu ⇒ dy du = 1 u substitute these values into (A) changing u back to terms of x ⇒ dy dx = 1 u (2x) = 2x 1 x2 Answer link\lim _{x\to 0}(x\ln (x)) \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} stepbystep x\frac{dy}{dx}=y^{2} en Related Symbolab blog posts My Notebook, the Symbolab way Math notebooks have been around for hundreds of years You write down problems, solutions and notes to go backSolutionput (xy)=v then differentiate both sides with respect to 'x' we get 1dy/dx=dv/dx or, dy/dx=dv/dx—1 this value put in to equation (I), first arranging equation (I) dy/dx= (xy1) (xy—2)/ (xy2) (xy—1) or, dv/dx—1= (v1) (v—2)/ (v2) (v—1) or,dv/dx= (v^2—2vv—2)/ (v^22v—v—2) 1



1




Y Ln X Dx Dy Y 1 X 2 Ayudaa Con Esta Ecuacion Doy 5 Puntoos Graciias Brainly Lat
Y2 = x−lnx1c (110) ylnx dx dy = µ y 1 x ¶ 2, ylnxdx= (y 1)2 x2 dy, (y 1)2 y dy = x2 lnxdx, Z (y 1)2 y dy = Z x2 lnxdx, resolvemos la integral del lado izquierdo Z (y 1)2 y dy = Z y2 2y 1 y dy = Z µ y 2 1 y ¶ dy = y2 2 2y lny, resolvemos la integral del lado derecho Z x2 lnxdx= integral por partes, tomamos u =lnxdu= 1 xSee the answer See the answer See the answer done loadingFor the graph in (figure 1) determine the frequency f Which of the following is a polynomial;



1



Ln Rules
To find the opposite of d x 2 y d x, find the opposite of each term xdydy^ {2}dx^ {2}ydx=0 x d y − d y 2 − d x 2 − y d x = 0 Combine xdy and ydx to get 0 Combine x d y and − y d x to get 0 dy^ {2}dx^ {2}=0 − d y 2 − d x 2 = 0 Add dy^ {2} to both sides Anything plus zero gives itselfFind dy/dx y=x^2e^x y = x2ex y = x 2 e x Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx (x2ex) d d x ( y) = d d x ( x 2 e x) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps Differentiate using the Product Rule which states that d d x f ( x) g ( xCalculus Find dy/dx y=1/x y = 1 x y = 1 x Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx ( 1 x) d d x ( y) = d d x ( 1 x) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps



Secure Media Collegeboard Org



How To Solve The Differential Equation Dy Dx Y 1 X X 1 2 1 X 1 2 Quora
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high 100% (13 ratings)#NON #EXACT #INTEGRATING FACTORLearn how to solve differential equations problems step by step online Solve the differential equation (y^21)dx=ysec(x)^2*dy Group the terms of the differential equation Move the terms of the y variable to the left side, and the terms of the x variable to the right side of the equality Simplify the expression \frac{1}{\frac{y^21}{y}}dy Simplify the expression



How To Solve Dy Dx 1 Xy Y X Quora
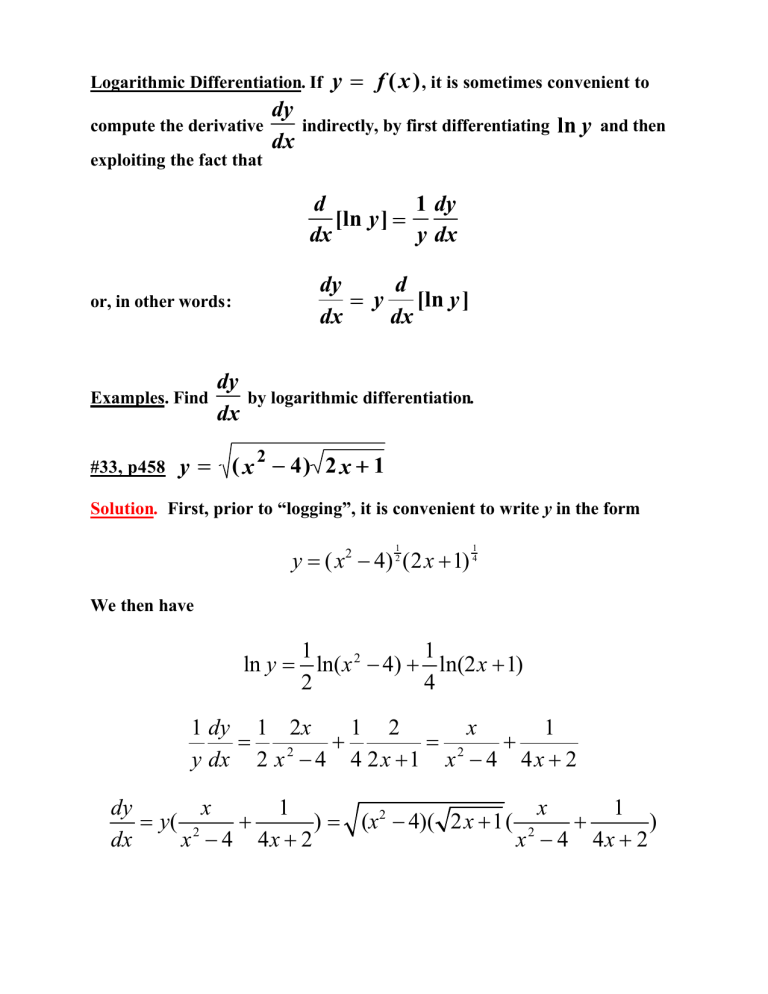



Ln Y Dy Dx 2
What is the speed of a 50mev h−? To ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW `(dy)/(dx)=(xy)ln(xy)1`Dy/dx y = (1 y) /x yields dy/dx (1 1//x) y = 1/x so that P = 1 1/x and Q = 1/x Then the integrating factor is v (x) = e ^ {Integral P (x) dx = e^ x ln x = x e^x The solution is given by yv = Integral Qv} ie y (xe^x) = Integral e^x dx = e^x c Finally y = 1 c e^ (x) / x 11K views




Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf Free Download



Lcps Org
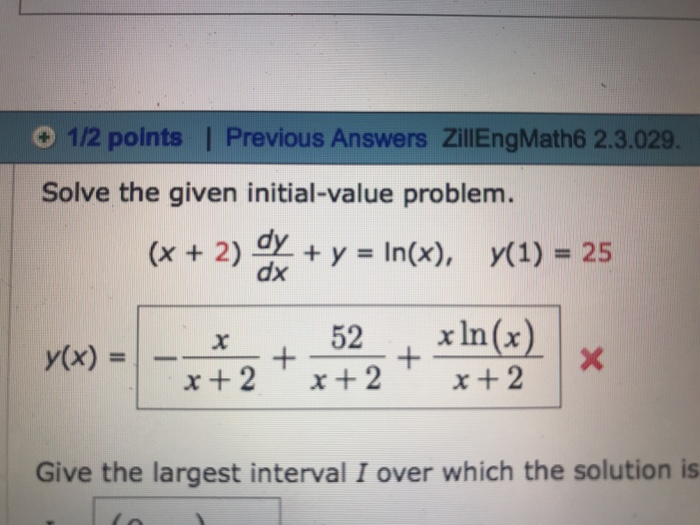
Solved For the following exercises, use logarithmic differentiation to find (dy)/(dx) y=(x^21)^(ln x)See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading Solve the given initialvalue problem (x 3) dy/dx y = ln (x), y (1) = 30 y (x) = Expert Answer Who are the experts? Explanation For d dt d dt (ln(x2 y2)) = 1 x2 y2 d dt (x2 y2) = 1 x2 y2 ⋅ (2x dx dt 2y dy dt) For d dx d dx (ln(x2 y2)) = 1 x2 y2 d




Separable Differential Equations Yln X Dx Dy Y 1 X 2 Youtube



How To Solve This Equation 3x Dy Dx Y Lnx 1 Quora
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreTo ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW `(1x^2)dy/dx=1y^2`Calculus Find dy/dx y^2= (x1)/ (x1) y2 = x − 1 x 1 y 2 = x 1 x 1 Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y2) = d dx ( x−1 x1) d d x ( y 2) = d d x ( x 1 x 1) Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more steps




Ex 9 5 12 Find Particular Solution X2 Dy Xy Y2 Dx 0
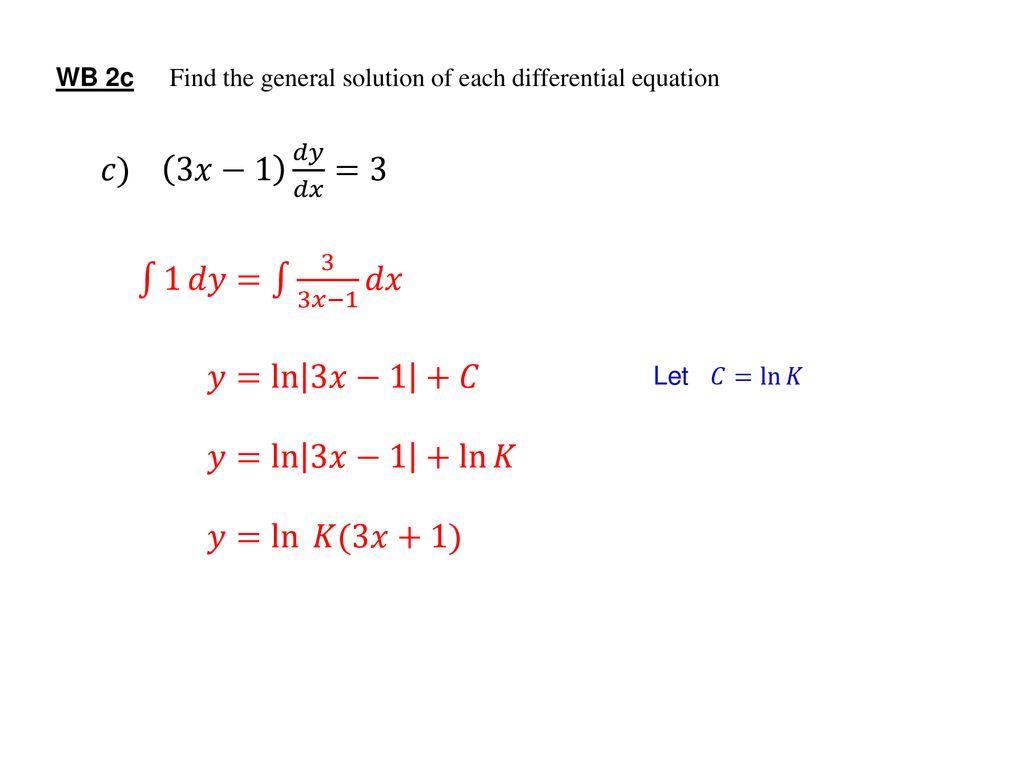



Differential Equations Ppt Download
To ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW `x(1y^2)dxy(1x^2) dy=0`Learn how to solve differential equations problems step by step online Solve the differential equation dy/dx=(2x)/(3y^2) Take \\frac{2}{3} out of the fraction Rewrite the differential equation in the standard form M(x,y)dxN(x,y)dy=0 The differential equation y^2dy\\frac{2}{3}xdx=0 is exact, since it is written in the standard form M(x,y)dxN(x,y)dy=0, where M(x,y) and N(x,y) areDy dx = x2 y = x2 {z} g(x) 1 y {z} f(y) 2 Separate the variables y dy = x2 dx 3 Integrate both sides Z y dy = Z x2 dx y2 2 = x3 3 C 0 4 Solve for y y2 2 = x3 3 C 0 y2 = 2x3 3 C y = r 2x3 3 C Note that we get two possible solutions from the If we didn't have an initial condition, then we would leave the 2in the nal answer, or
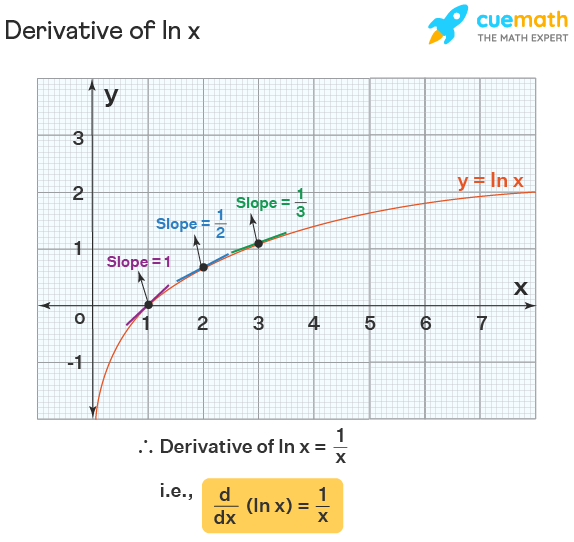



Derivative Of Ln X Formula Proof Examples



Find The Area Of The Region Enclosed By Y Ln X The X Axis The Y Axis And Y 1 A Dx Select B Dy Select Socratic
(1) Let y = xv then dy/dx = x (dv/dx) v Substitute in (1), you get x(dv/dx) v = (xv x)/(xv x) = (v 1)/(v 1) Thus x(dv/dx) = (v 1)/(v 1) v = (v 1 v^2 v)/(v 1) = (v^2 1)/(v 1) and (v 1)/(v^2 1) dv = dx/x and v/(v^2 1Calculadora gratuita de derivadas – derivar funções com todos os passos Digite qualquer derivada para obter solução, passos e gráficoDownload Solution PDF Consider the following statements 1 If y = ln (sec x tan x), then d y d x = sec x 2 If y = ln (cosec x cot x), then d y d x = c o s e c x Which of the above is / are correct?




Solve Y 1 Xy Dx X 1 Xy X 2y 2 Dy 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Differential Equations Seperable Equations A Y Tan Ln X 5 5 B Y 31 Es2 Ds 27 3 Homeworklib
See the answer See the answer done loading Sketch the region of integration 6 1 ln ( x) f ( x, y) dy dx 0 Change the order of integrationMost Used Actions \mathrm {implicit\derivative} \mathrm {tangent} \mathrm {volume} \mathrm {laplace} \mathrm {fourier} See All area asymptotes critical points derivative domain eigenvalues eigenvectors expand extreme points factor implicit derivative inflection points intercepts inverse laplace inverse laplace partial fractions range slope\lim _{x\to 0}(x\ln (x)) \int e^x\cos (x)dx \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n} stepbystep implicit derivative \frac{dy}{dx}, (xy)^2=xy1 en Related Symbolab blog posts Practice, practice, practice Math can be an intimidating subject Each new topic we learn has symbols and problems we have never seen The unknowing



How To Solve X Y 1 Dy X Y 1 Dx Quora




Solved The General Or Particular Solution As Corresponds 1 Sx 4y Dx 4x 8y3 Dy 0 2 Ex Y Dx 2 X Yey Dy 0 Y 0 1 3
Find dy/dx y=x natural log of x y = xln (x) y = x ln ( x) Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx (xln(x)) d d x ( y) = d d x ( x ln ( x)) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps Differentiate using the Product Rule which states thatFind dy/dx y = natural log of x^2 y = ln (x2) y = ln ( x 2) Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (y) = d dx (ln(x2)) d d x ( y) = d d x ( ln ( x 2)) The derivative of y y with respect to x x is y' y ′ y' y ′ Differentiate the right side of the equation Tap for more steps Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that This means the derivative of ln(lnx) is 1 x ⋅ lnx This gives us the derivative of ln(lnx) ⋅ lnx which is lnx x ⋅ lnx ln(lnx) x If we do some cancellation we get 1 x ln(lnx) x, but since they both have denominators of x we can combine them to get ln(lnx) 1 x THIS is the derivative of the original exponent which we will multiply



Www3 Nd Edu




How Do You Find Dy Dx For Y 2x Sqrt X 1 Socratic
The equation can be written in normal form as dy/dx (x1)y/x = x , x # 0The integrating factor is xe^ (x) and the solution is given by y = ( (e^x)/x) Integral of (x^2)e^ (x)dx C = ( (e^x)/x) (e^x) (x^22x2)CThen the solution is y = ( Ce^x x^2 2x 2 )/x 642 views ·Mathematics is Life Subhasish Debroy , Former SDE at Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited Answered Apr 12 Author has 43K answers and 29M answer views ln (xy) = xy differentiating both sides wrt x 1/ (xy)d/dx (xy) = d/dx (xy) => 1/xy x dy/dxy = 1 dy/dx => 1/x 1/y (dy/dx) –



If Y X N 1 Lnx Then Prove That X 2 D 2y Dx 2 3 2n X Dy Dx N 1 2y 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
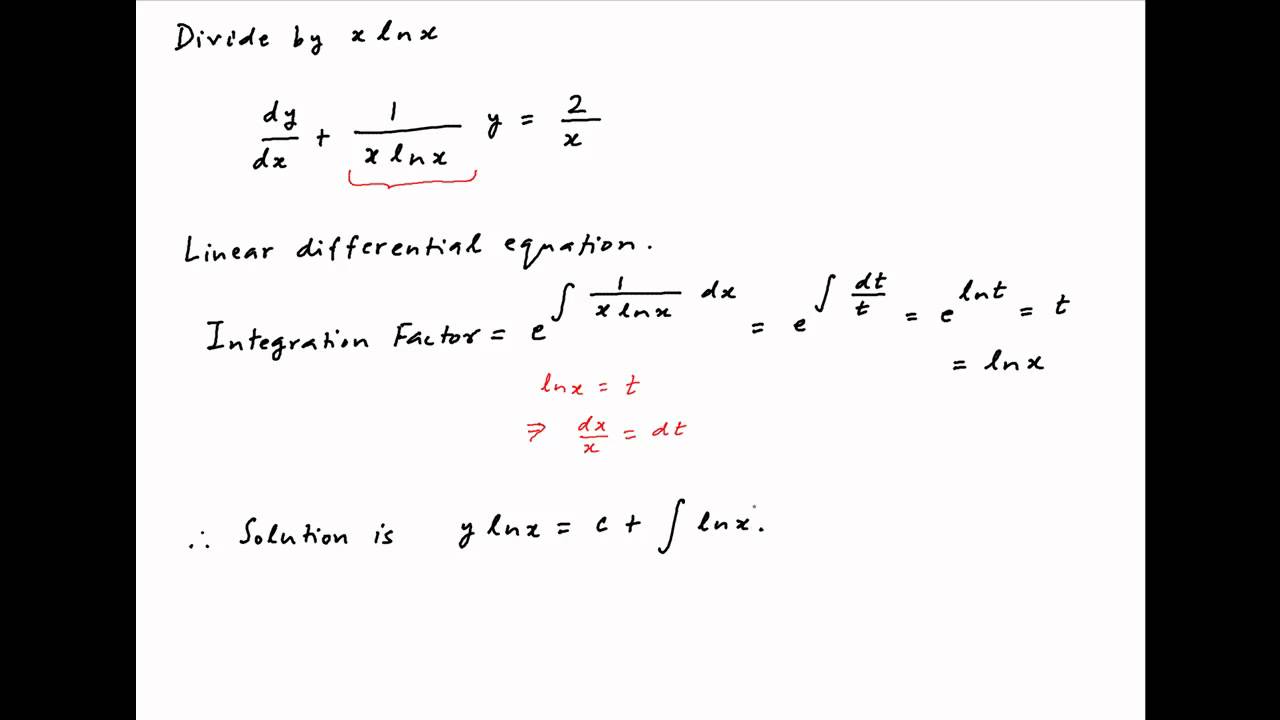



Solve The Differential Equation Xlnx Dy Dx Y 2lnx Youtube




Find Y X If It Satisfies The Following Differential Equation Dy Dx X Y 2 And Given That Y 1 1 A Ln 1 X Y 1 X Y 2 X 1 B Ln 2 Y 2 X X Y 1 C Ln 1 X Y 1 X Y 2 X 1 D 1 2ln 1 X Y 1 X Y Ln X 0




Hwkwliysgsum



Secure Media Collegeboard Org



Solved Solving Exact First Oder Differential Equations 2xydx X 2 Cosy Dy 0 Y Xy 2 1 1 X 2y 2x Y Dx X 3y Dy 0 2x Y 4 Dx X 3y 12 Dy 0 Ye X S Course Hero
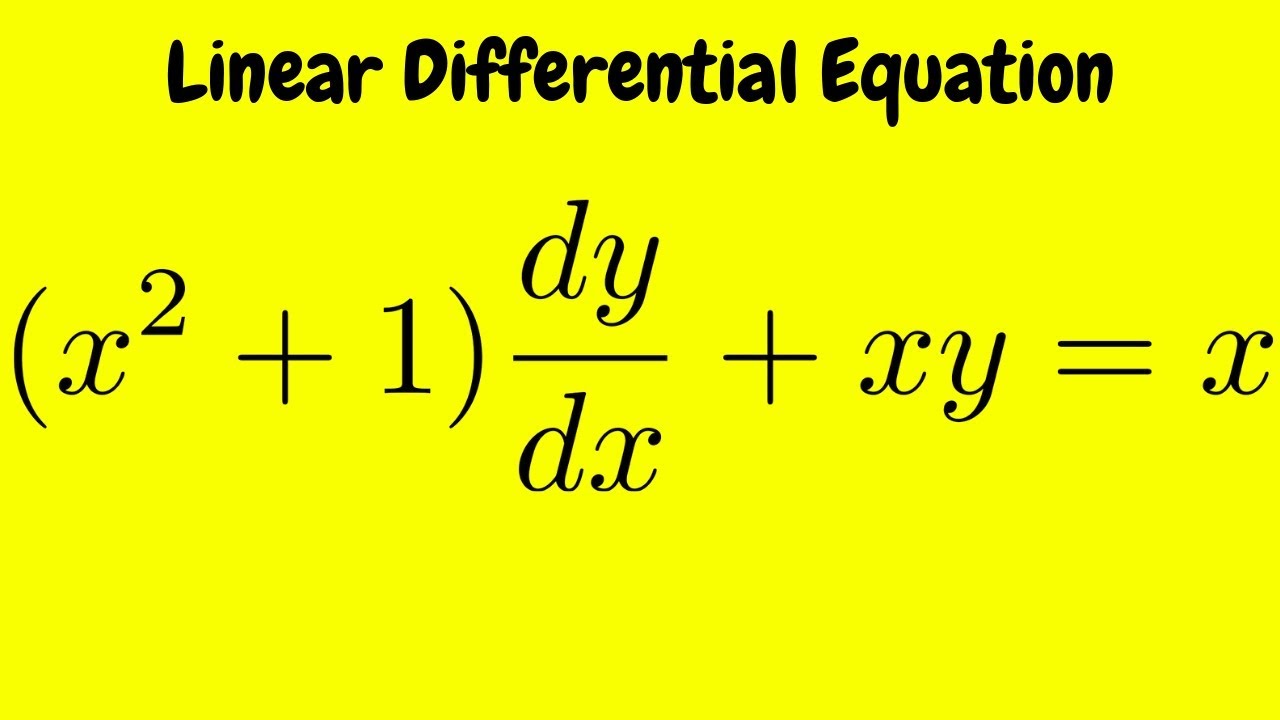



Solve The Linear Differential Equation X 2 1 Dy Dx Xy X Youtube




Solved Solve The Given Initial Value Problem Give The Chegg Com
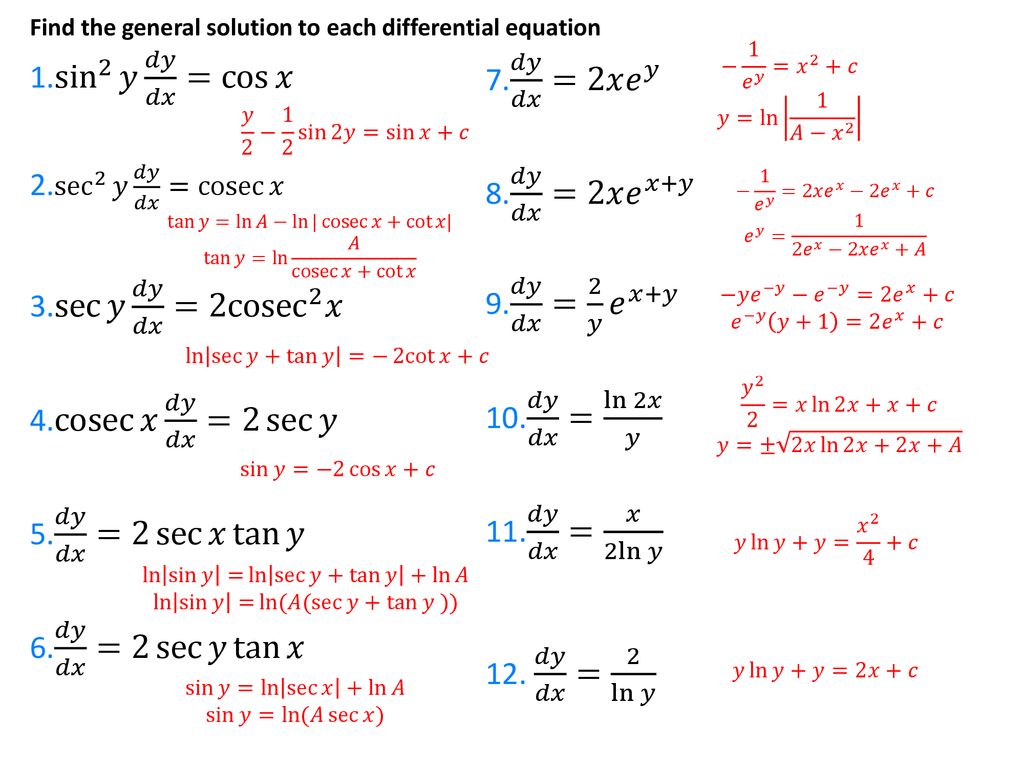



Differential Equations Separation Of Variables Ppt Download



Math Colostate Edu



X Y 2 Graph



How To Solve The Equation Dy Dx 1 X Y X Y Quora




8 1 Ln X Y X Dx 1 Ln X Dy Ecuaciones Exactas Alexander Estrada Youtube



Solve 1 X 2d 2y Dx 2 1 X Dy Dx Y 2sin Log 1 X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Solved Solve The Following Bernoulli Equations B 2 X 2 Dy Dx Xy X 3 Y 3 C Y X Y X2 5 X 2 Y 1 2 D X Dy Dx 6y 3xy Course Hero



Solved Find The Particular Solution Of Y 2x 2 Xy Y 2 Dx X 2 2x 1 Dy 0 When X 1 Y 1 2 Find The Particular Solution Of 16x 5y Dx 3x Y Dy 0 Course Hero




Solved Y Ln Y X 2 1 Dy Dx 2xy Y 1 X 2 Y 2 4 Chegg Com
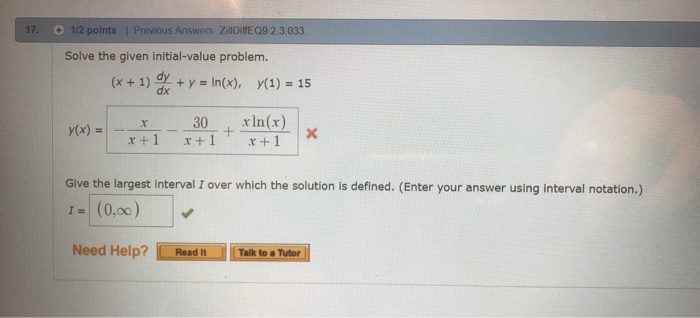



Solved Solve The Given Initial Value Problem X 1 Dy Dx Chegg Com




Help Asap If Dy Dx 2 Y And If Y 1 When X 1 Then Y Photo Attached Brainly Com
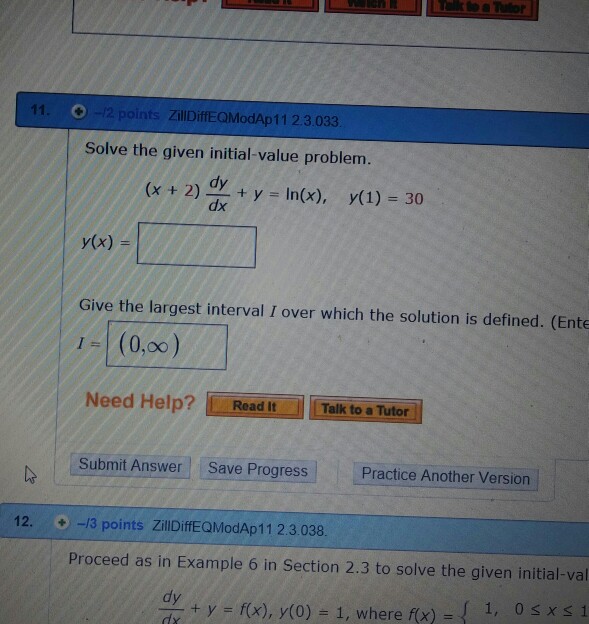



Solved Solve The Given Initial Value Problem X 2 Dy Dx Chegg Com




Chegg Com Studying Math Maths Algebra Math Quotes




Separable Equations Example Old Video Khan Academy



Ucl Ac Uk




Solve Dydx Y 2 With Y 1 1



Amherst Edu
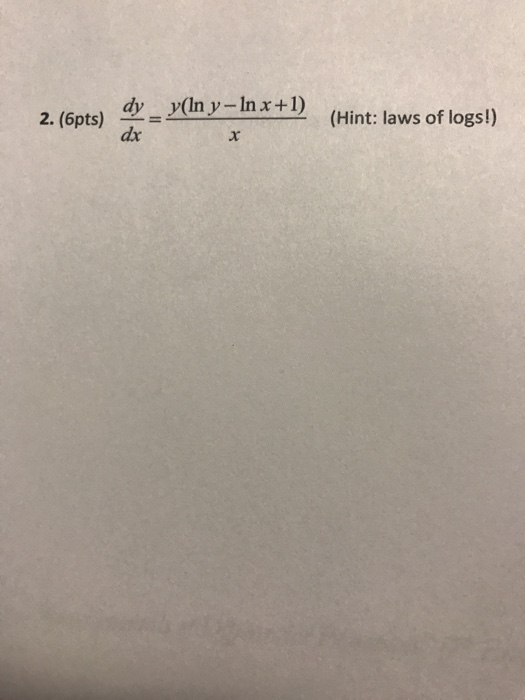



Solved Dy Dx Y Ln Y Ln X 1 X Chegg Com




Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions




33 X 1 Dy Dx Y Ln X Y 1 10 Ecuaciones Lineales Alexander Estrada Youtube



Solve 2x Y 1 Dx 2y X 1 Dy 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Ppt Exam 2 Fall 12 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
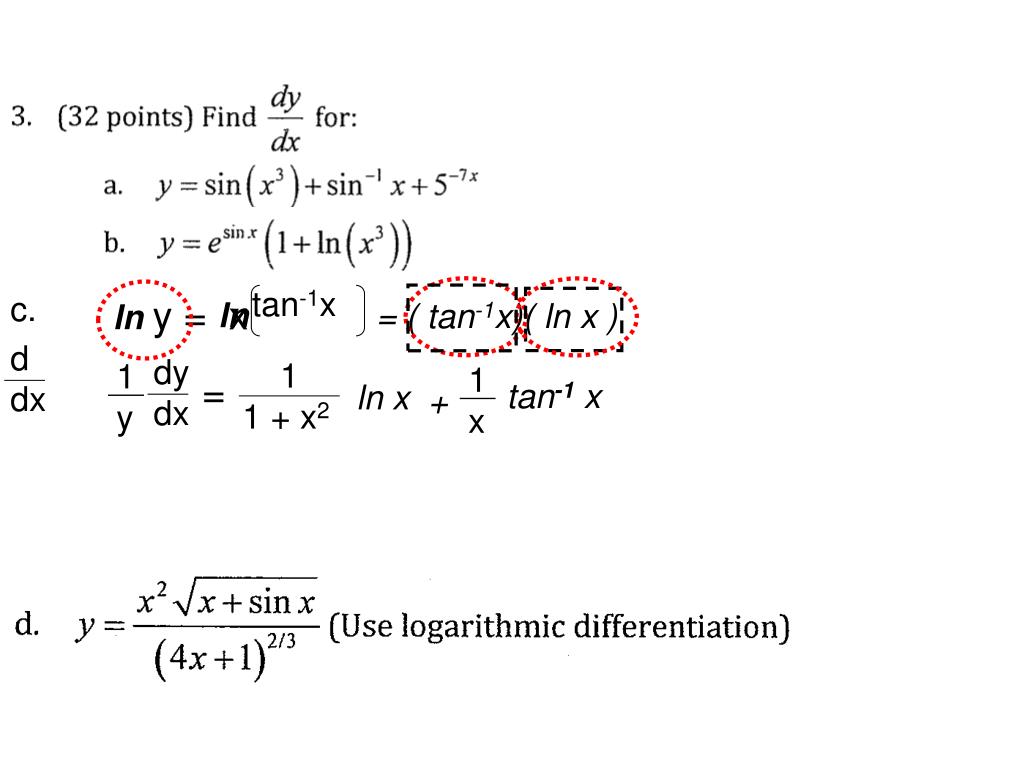



Ppt Exam 2 Fall 12 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Webassign Net




Worked Example Identifying Separable Equations Video Khan Academy
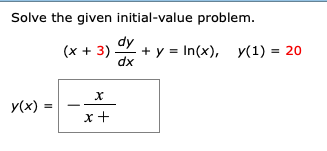



Solved Solve The Given Initial Value Problem X 3 Dy Dx Chegg Com



How To Find Dy Dx Of The Function Y X 1 X 2 X 1 2 Quora
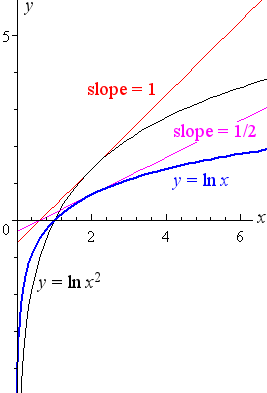



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function




The Solution Of Dy Dx X 2 Y 2 2x 2 Is
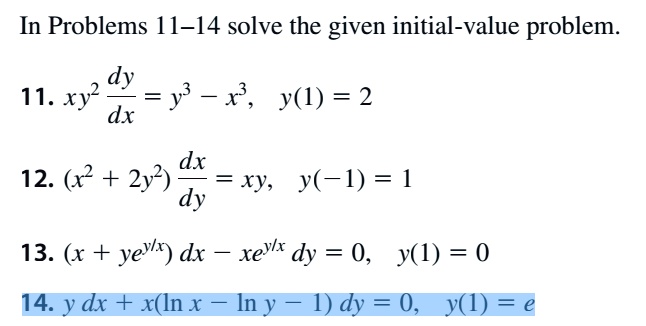



Solved In Problems 11 14 Solve The Given Initial Value Problem Dy 11 Xy2 Y X Y 1 2 Dx 12 2 2y Dx Xy Y 1 1 Dy 13 X Yeyx Dx
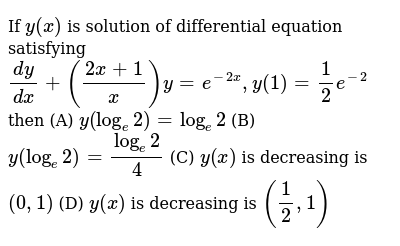



If Y X Is Solution Of Differential Equation Satisfying Dy Dx 2x 1 X Y E 2x Y 1 1 2e 2 Then A Y Log E2 Log E2 B Y Log E2 Log E2 4 C Y X Is Decreasing Is 0 1 D Y X Is Decreasing Is 1 2 1




Homogeneous Differential Equations




Engineering Mathematics Notes



How To Solve This Differential Equation Y Xy Dx X X Y Dy 0 Quora
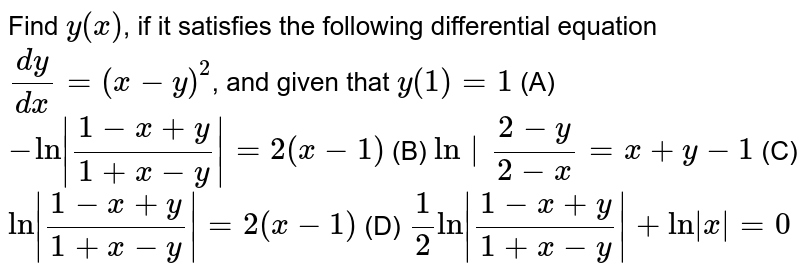



Find Y X If It Satisfies The Following Differential Equation Dy Dx X Y 2 And Given That Y 1 1 A Ln 1 X Y 1 X Y 2 X 1 B Ln 2 Y 2 X X Y 1 C Ln 1 X Y 1 X Y 2 X 1 D 1 2ln 1 X Y 1 X Y Ln X 0



Secure Media Collegeboard Org



Solved Solving Exact First Oder Differential Equations 2xydx X 2 Cosy Dy 0 Y Xy 2 1 1 X 2y 2x Y Dx X 3y Dy 0 2x Y 4 Dx X 3y 12 Dy 0 Ye X S Course Hero
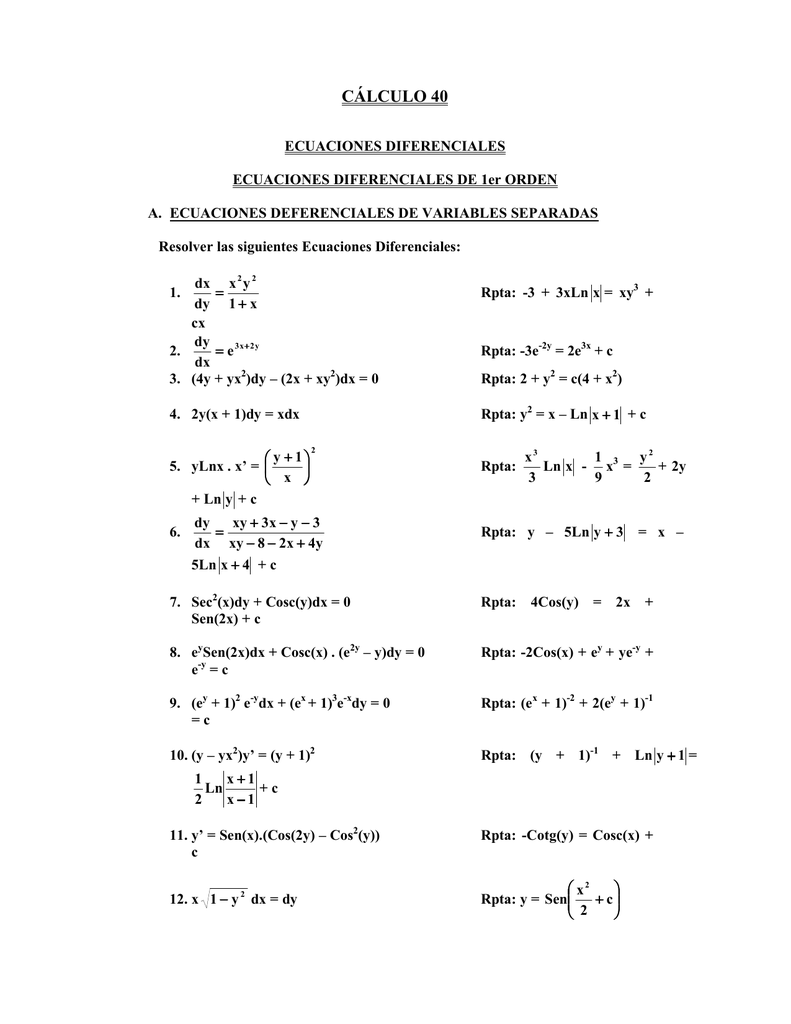



最新 Xy1 試す



Ualberta Ca




9 Ylnx Dy Dx Y 1 X 2 Variables Separables Separable Variables Youtube




Ii Y Ln Y D X X L N Y D Y 0




Oneclass A Variable Separable Equations Xy X Dx X2y2 X2 Y2 1 Dy Select One A 21n X2 1




Graph The Equation Y Ln X 1 And Identify Its Domain And Asymptote Study Com
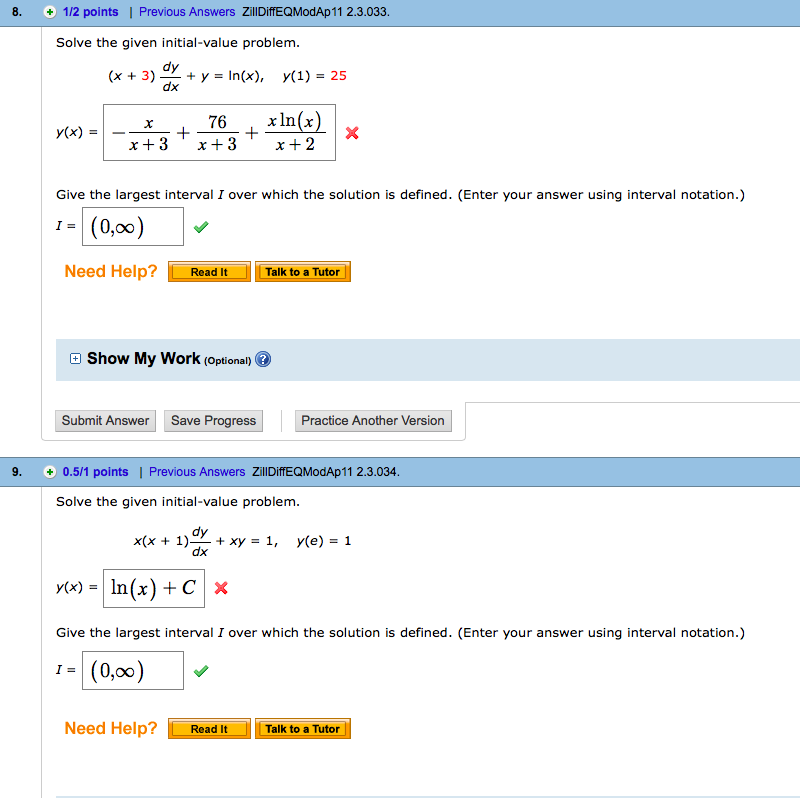



Solved 8 1 2 Points Previous Answers Zilidiffeqmodap11 Chegg Com
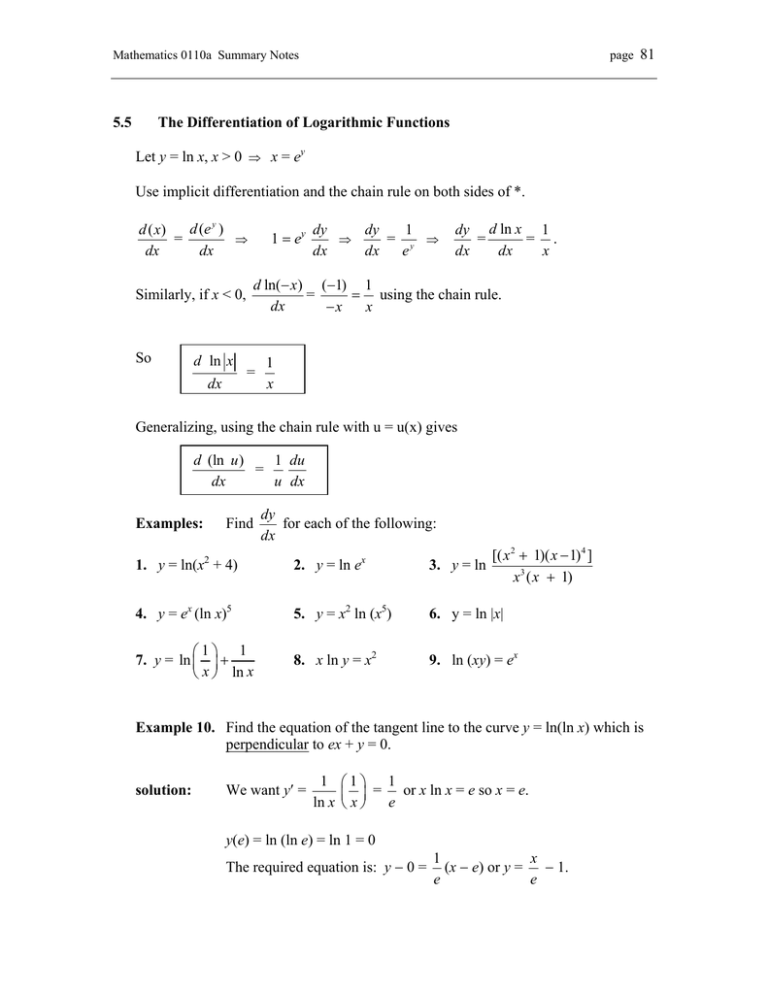



5 5 The Differentiation Of Logarithmic Functions Let Y Ln X X 0




Engineering Mathematics Notes




Find Frac Dy Dx At X 1 When Sin Y Sin Pi X 2 Frac Sqrt 3 2 Sec 1 2x 2 X Tan Ln X 2 0 Snapsolve



Secure Media Collegeboard Org
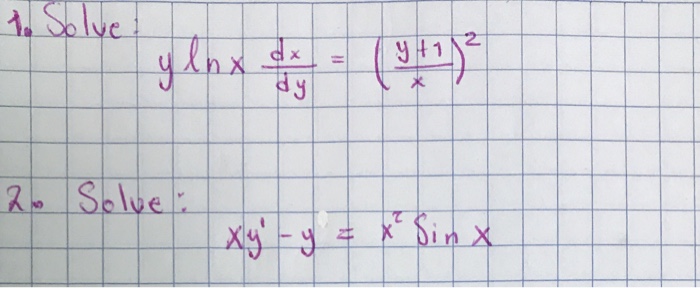



Solved Solve Y Ln X Dx Dy Y 1 X 2 Solve Xy Y Chegg Com
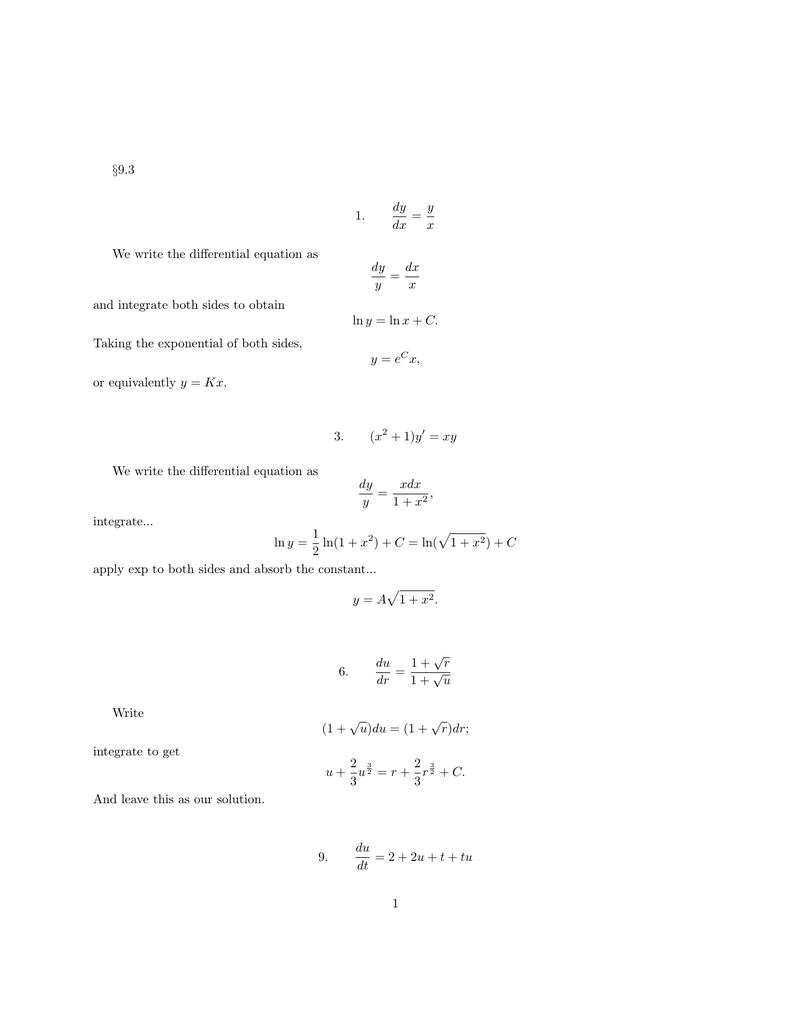



9 3 1 Dy Dx Yx We Write The Differential Equation As Dy Y Dx X And




Derivative Of Ln X Natural Logarithm More




Persamaan Pembezaan
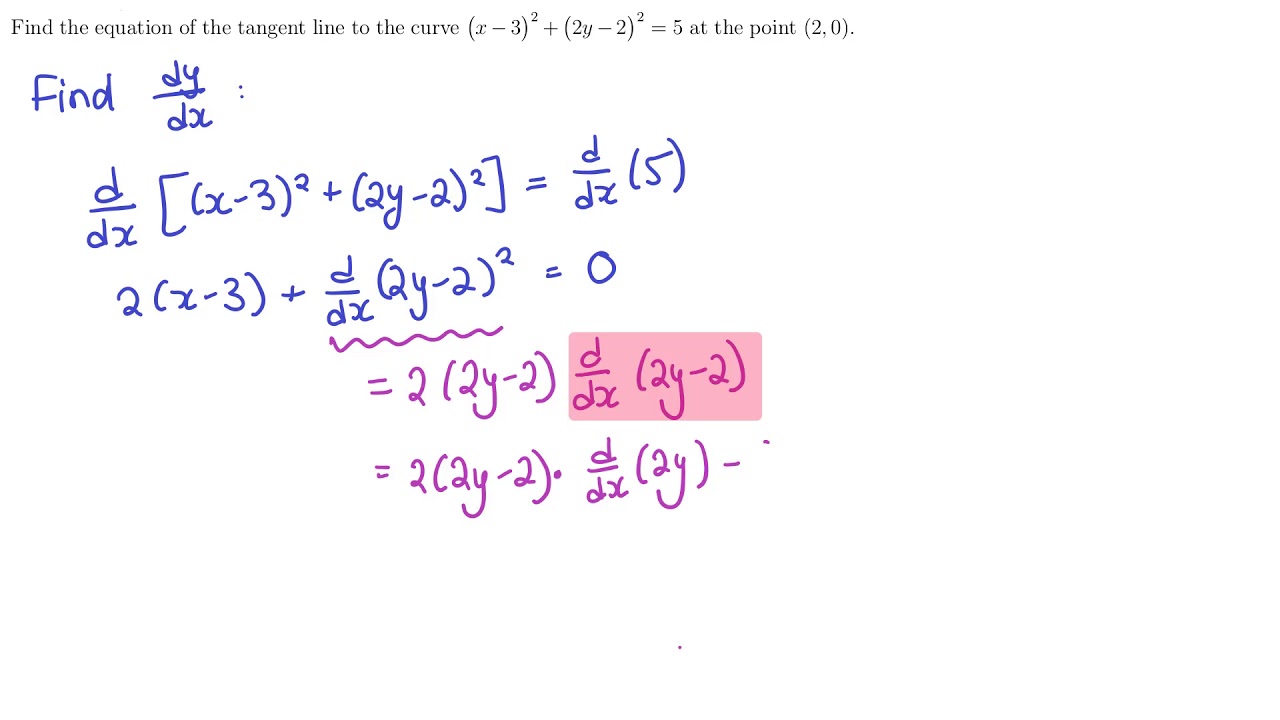



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation
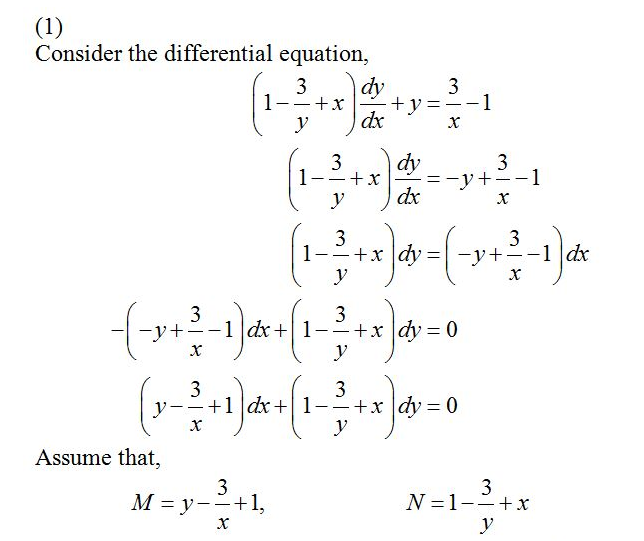



Solve The Following Differential Equation 1 1 3 Y X Dy Dx Y 3 X 1 2 Ln X Y X Dx Ln X Dy 3 X 2 Y 2 Y 4sin X Dx 2xy 4y 3cos X Dy 4 Tan X 8sin X Sin Y Dx 8cos X Cos Y Dy 0 5 1 Y 2sin 2x Dx Ycos 2x Dy 0 Wegglab



How To Solve This Differential Equation Math Y Ln Y Ln X 1 Dx Xdy 0 Math Quora




Solucionario Ecuaciones Diferenciales




Differential Equations Ppt Download




Derivative Of Ln X Lnx 2 1 Lnx More
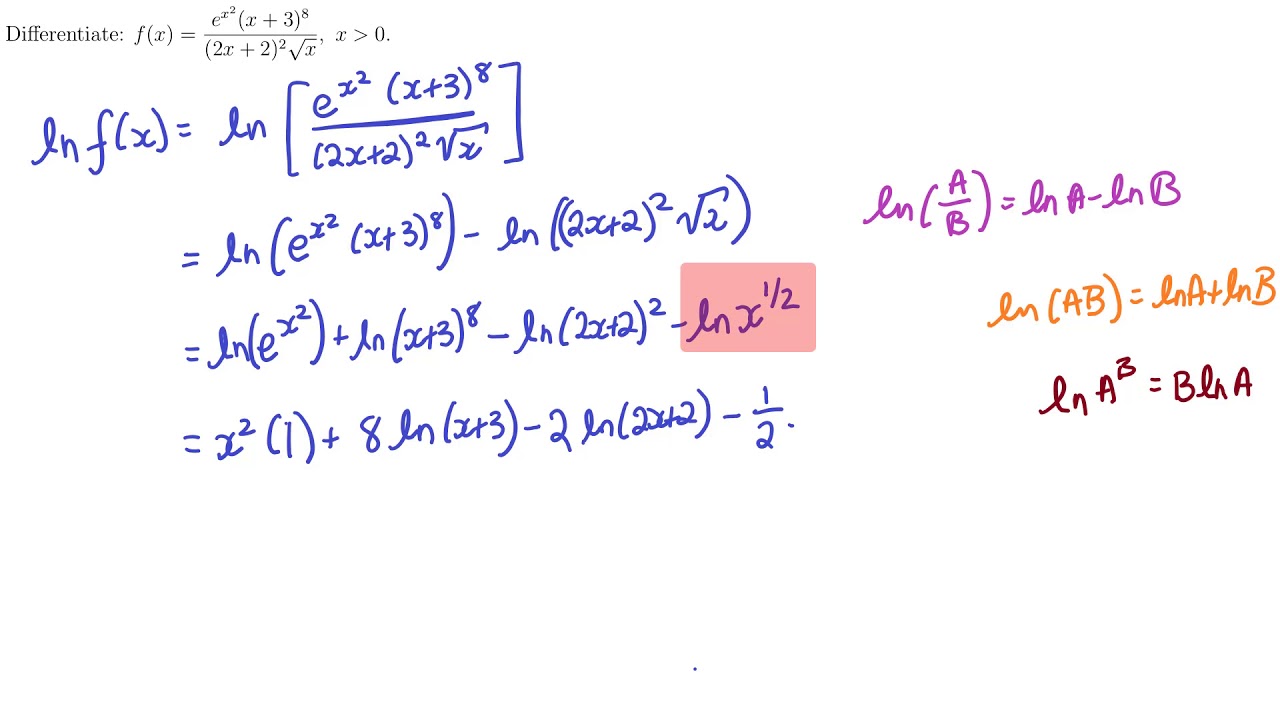



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation
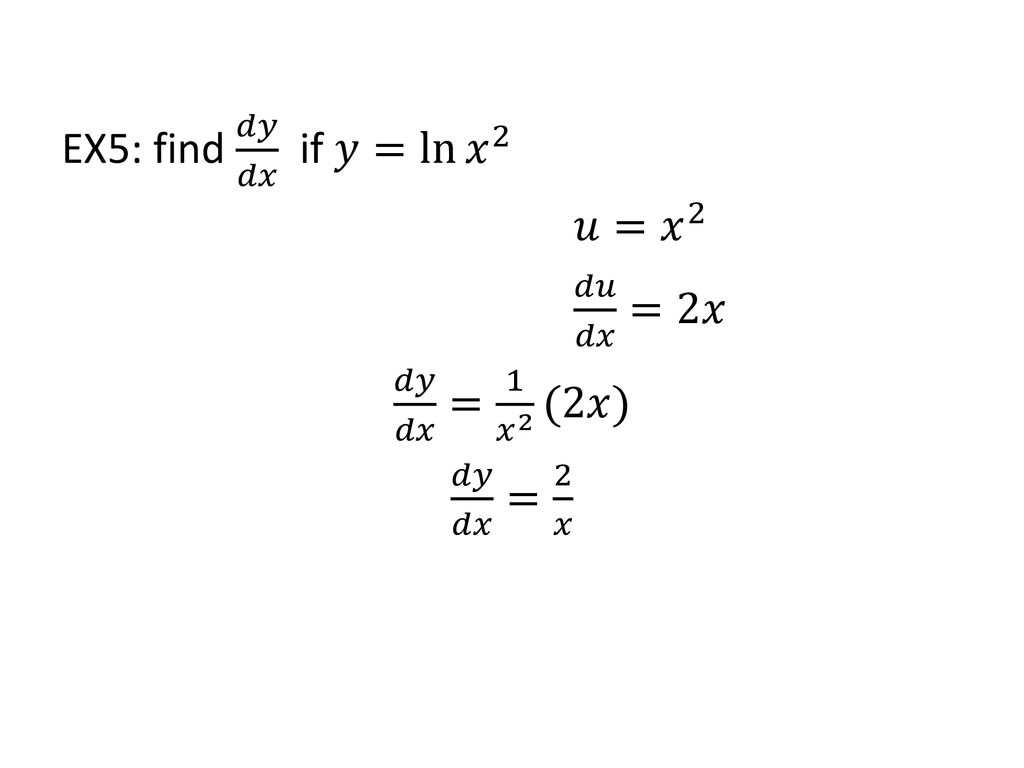



Derivatives Of Ppt Download




Differential Equations Solved Examples Dy Dx 1 X 2 3x Y 4 2 3 Ln 4



Differential Equations Separation Of Variables Ppt Download
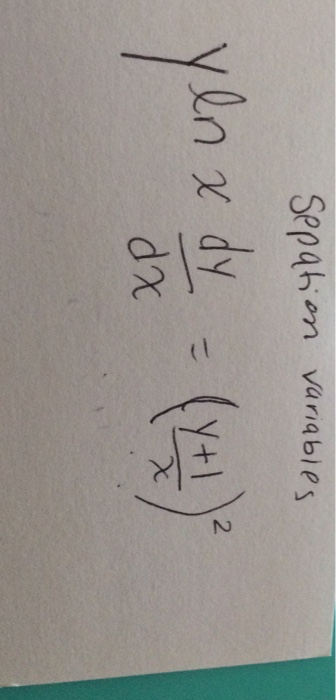



Solved Separation Variables Y Ln X Dy Dx Y 1 X 2 Chegg Com
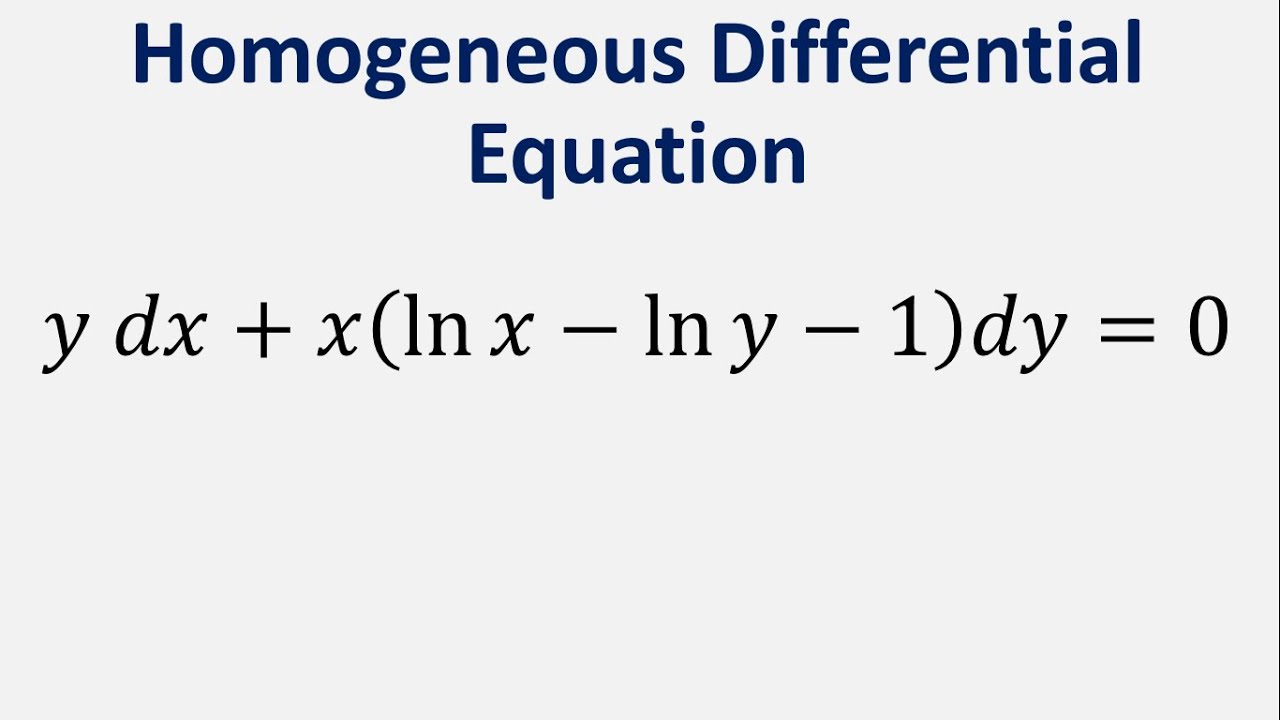



Homogeneous Differential Equation Y Dx X Ln X Ln Y 1 Dy 0 Youtube



Www3 Nd Edu



Solved リ1 2 Points Previous Answers Zilengmath6 2 3 029 Chegg Com



Find The Area Of The Region Enclosed By Y Ln X The X Axis The Y Axis And Y 1 A Dx Select B Dy Select Socratic




1 Solve The De 4y 2x 5 Dx 6y 4x 1 Dy 0 Subject To Y 1 2 2 Given The De X Y Dx X Ln X Dy Mdx Ndy 0 A Compute Mu X E Int K X Dx Where K X Frac Frac Delta M Delta Y Frac



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function




Show That Z Ln X 2 Y 2 2 Tan 1 Y X Satisfies The Laplaces S Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿